|
Creating a 3D Score Plot
Overview
The 3D Score Plot is a scatter plot. The x, y and z axes represent individual Principal Components (PCs). The plot contains points that represent the original data (projected Samples if PCA by Genes or projected Genes if PCA by Samples) projected onto the individual PCs. By default, the 3D Score Plot shows data on the first three PCs.
Actions
1. Double-click a PCA experiment in the Experiments navigator. The item is highlighted and a 3D score plot of the selected item is displayed.
OR
1. Click a PCA experiment in the Experiments navigator. The item is highlighted.
2. Click the 3D Score
Plot toolbar icon ![]() , or select 3D
Score Plot from the PCA
menu, or right-click the item and select 3D
Score Plot from the shortcut menu. A 3D score plot of the selected
item is displayed.
, or select 3D
Score Plot from the PCA
menu, or right-click the item and select 3D
Score Plot from the shortcut menu. A 3D score plot of the selected
item is displayed.
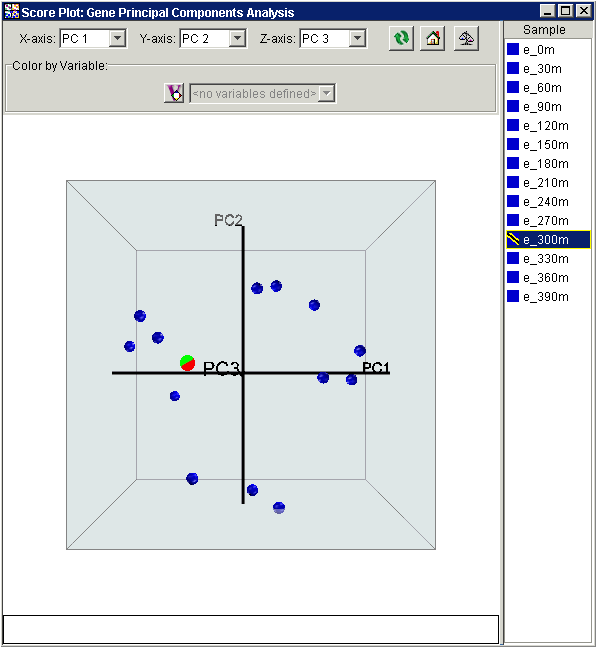
The text area at the bottom of the plot displays the first three principal component values for the point the mouse cursor is pointing at.
Normalizing the Data
The Raw
Data/Normalize button ![]() in the upper right corner
of the plot acts as a switch between two views of the data: raw and normalized.
The button 'pressed' state displays the normalized view, the 'unpressed'
state shows the raw view.
in the upper right corner
of the plot acts as a switch between two views of the data: raw and normalized.
The button 'pressed' state displays the normalized view, the 'unpressed'
state shows the raw view.
1. Click the Raw Data/Normalize button. A normalized view of the data is displayed.
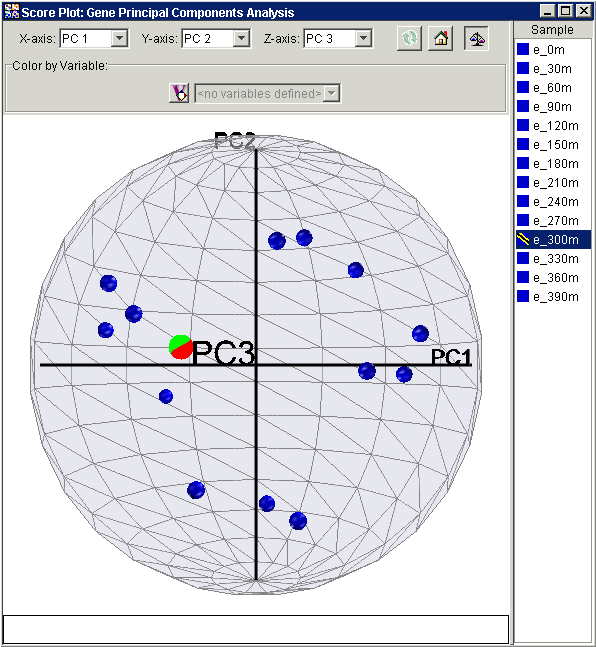
The normalized view is strictly analogous to, and presents the same information as, the raw view. The essential difference is that in the normalized view, before the points are plotted, the projected values are divided by the Euclidean norm, i.e., vector length, of the respective row of Samples (if PCA by Genes) or respective column of Genes (if PCA by Samples).
In some cases, the PCs can be interpreted biologically. This normalized view allows you to easily identify the genes or samples that share the properties of the PCs selected for axes of the plot.
Values close to 1 (one) for any normalized view indicate that the sample or gene is almost parallel to the principal component; -1 implies anti-parallel. This view provides a relative measure of how closely correlated each Sample (if PCA by Genes) or Gene (if PCA by Samples) is to an axis PC.
Note: The term ‘normalized’ here refers to the re-scaling of projections for the 3D Score Plot. It does not refer to any normalizations of the raw data that may, or may not, have been done prior to performing the PCA.
Note: Plotting a PC against itself may correctly result in points falling outside the unit circle. This is the only case that will do so. Plotting a PC against itself provides no useful information.
Home Button
The Home
 button returns the plot to its original orientation.
button returns the plot to its original orientation.
Refresh Button
The Refresh
 button refreshes the display after you change the choice
of principal components.
button refreshes the display after you change the choice
of principal components.
Changing the PCs
To change the PC represented by the X-axis, click on a PC in the X-axis drop-down list in the upper left corner of the plot. Click the Refresh button to update the plot.
To change the PC represented by the Y-axis, click on a PC in the Y-axis drop-down list in the upper center of the plot. Click the Refresh button to update the plot.
To change the PC represented by the Z-axis, click on a PC in the Z-axis drop-down list in the upper center right of the plot. Click the Refresh button to update the plot.
Plot Functions
Related Topics:
Overview of Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Functionality
Tutorial 5: Principal Component Analysis (PCA)