|
Positive and Negative Control Genes
Overview
In some microarray experiments, there may be one or more control genes that can be used to normalize between samples. With multiple controls, the median or mean is calculated over all of the controls.
The control genes are always discarded prior to returning the normalized dataset.
Normalization Relative to Negative Controls
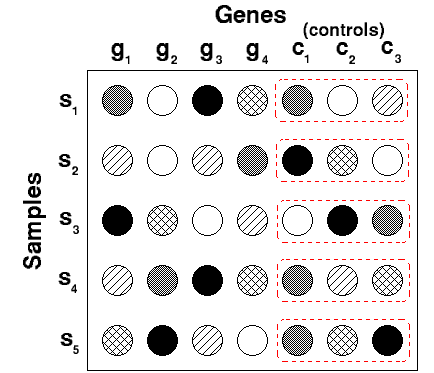
For each sample, this is done by subtracting the median or mean of the negative controls within the sample. If you have only one control gene, the median or mean of the negative control is the value itself.
For example:
Gene i sample j - median of the negative control genes within sample j
Gene i sample k - median of the negative control genes within sample k
Below is an example that illustrates the application with three control genes for each sample:
Normalization Relative to Positive Controls
For each sample, this is done by dividing the median or mean of the positive controls within the sample. If you have only one control gene, the median or mean of the positive control is the value itself.
For example:
Gene i sample j / median of the positive control genes within sample j
Gene i sample k / median of the positive control genes within sample k
Refer to the above image.
Normalization Relative to Negative Controls Across Experiments
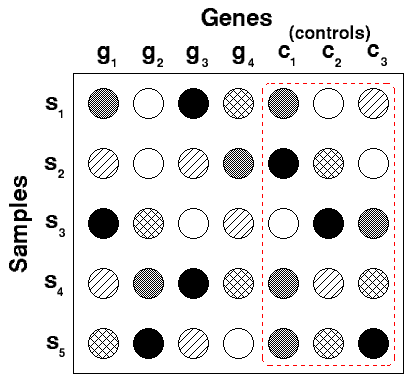
This is done by subtracting the median or mean of the negative control (one sample at a time) from all the values in the dataset.
For example:
Gene i sample j - median (all negative control genes across all samples)
Gene i sample k - median (all negative control genes across all samples)
Below is an image that illustrates the application with a single control for each sample:
Normalization Relative to Positive Controls Across Experiments
This is done by dividing the values in the dataset by the median value of the positive controls across all samples.
For example:
Gene i sample j /median (all positive control genes across all samples)
Gene i sample k / median (all positive control genes across all samples)
Refer to the above image.
Actions
1. Click a complete dataset in the Experiments navigator. The item is highlighted.
2. Click the Normalize
toolbar icon ![]() , or select Normalize
from the Data menu, or right-click
the item and select Normalize
from the shortcut menu. The first Normalization
dialog is displayed.
, or select Normalize
from the Data menu, or right-click
the item and select Normalize
from the shortcut menu. The first Normalization
dialog is displayed.
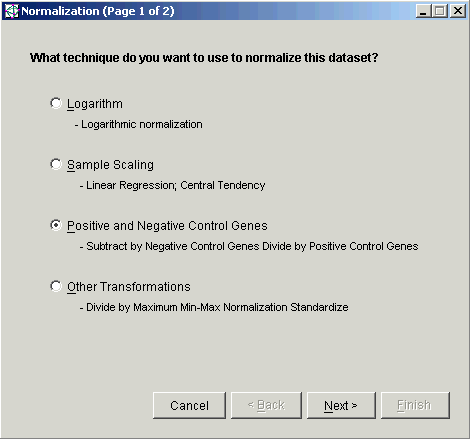
3. Double-click the Positive and Negative Control Genes radio button, or click it and click Next. The second Normalization dialog is displayed.
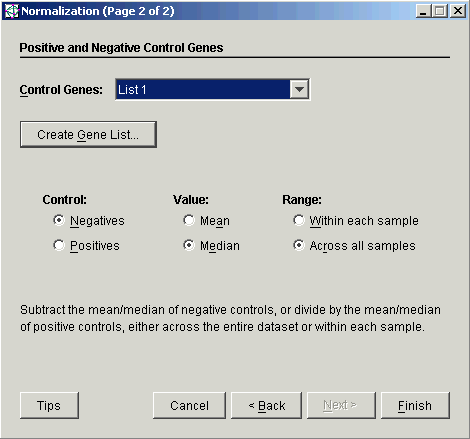
4. For this operation, you must select or create a gene list of the control genes. The gene lists listed in the drop-down list are only those lists that are relevant to this dataset (that is, the list contains one or more genes that are in the dataset).
To create a gene list:
a) Click the Create Gene List button. The Gene List Creator dialog is displayed.
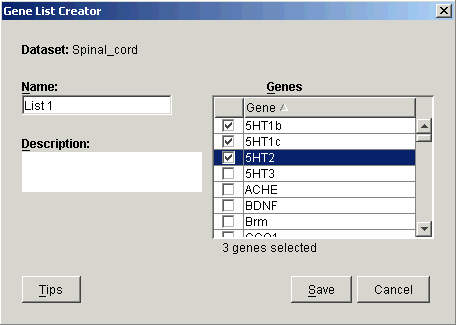
b) Type in a Name for the list and optionally a Description.
c) Click the checkboxes next to the genes to be included in the list.
d) Click Save. The gene list is then displayed in the Control Genes list on the Normalization dialog.
5. Select the Control type.
6. Select the Mean or Median for the Value.
7. Set the type of Range.
8. Click Finish. The Experiment Progress dialog is displayed. It is dynamically updated as the Control Genes Normalization operation is performed. To cancel the Control Genes Normalization operation, click the Cancel button.
If the operation cannot complete an error message is displayed. The operation will fail, for example, if the mean/median is zero or if the gene list contains all the genes in the dataset (the control genes are always discarded prior to returning the normalized dataset).
Upon successful completion, a new normalization dataset is added under the original dataset in the Experiments navigator.
Related Topics: