|
Division by Central Tendency (Mean)
Overview
This procedure scales the values across samples (gene chips) so that the mean or total intensity of each sample is equivalent. This is done for all samples.
This scaling is useful if you have reason to believe that the total amount of mRNA measured in each sample should be approximately equivalent, but there may be non-biological sample-dependent factors influencing the raw measurements. For instance, if your data contains an entire genome but your experimental conditions are only expected to perturb a small number of genes then this type of scaling may be useful. Similarly, if you expect a large number of genes to be perturbed but both up- and down-regulation are equally likely, then the total amount of mRNA will probably be constant and this would be a reasonable operation.
The fewer non-responding genes there are in your dataset, the less sound is this scaling. For instance, if your data has been pre-filtered to retain only genes known to be affected by the experimental conditions, then this normalization may introduce undesirable distortions into your data. In the same vein, we recommend that you apply this normalization before applying any variation filtering.
This normalization is usually only meaningful if applied to count data. We do not recommend applying this normalization to ratio data or data which has already been subject to a logarithm transformation, both of which may yield zero or negative values. Applying mean scaling to samples with negative means may yield drastically distorted data. Applying mean scaling to samples with zero or near-zero means will cause GeneLinkerô to fail to complete the operation, and generate an error message.
Before clustering, it is recommended that standardization be performed after mean scaling. Mean scaling makes the intensities across chips equivalent, but genes may still differ in absolute intensity, and standardization can address this.
Actions
1. Click a complete dataset in the Experiments navigator. The item is highlighted.
2. Click the Normalize
toolbar icon ![]() , or select Normalize
from the Data menu, or right-click
the item and select Normalize
from the shortcut menu. The first Normalization
dialog is displayed.
, or select Normalize
from the Data menu, or right-click
the item and select Normalize
from the shortcut menu. The first Normalization
dialog is displayed.

3. Double-click the Sample Scaling radio button, or click it and click Next . The second Normalization dialog is displayed.
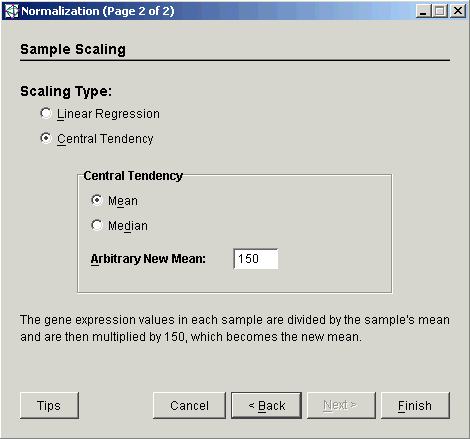
4. Select Central Tendency as the Scaling Type.
5. Set the Central Tendency to Mean.
6. Set the Arbitrary New Mean to the value to which the sample means should be scaled. The total intensity of each sample after scaling will be this number times the number of genes in the table.
7. Click Finish. The Experiment Progress dialog is displayed. It is dynamically updated as the Mean Scaling Normalization operation is performed. To cancel the Mean Scaling Normalization operation, click the Cancel button.
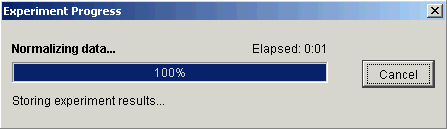
If the operation cannot complete an error message is displayed. The operation will fail, for example, if the mean of any sample is zero or near zero.
Upon successful completion, a new normalization dataset is added under the original dataset in the Experiments navigator.
Related Topics: