|
Performing Jarvis-Patrick Clustering
Overview
The Jarvis-Patrick clustering algorithm is good for detecting chain-like or non-globular clusters. It partitions data into clusters, generating a set of non-overlapping clusters.
For further details, see Overview of Jarvis-Patrick Clustering.
Actions
1. Click a complete dataset in the Experiments navigator. The item is highlighted.
2. Click the Partitional
Clustering toolbar icon ![]() , or select Partitional
Clustering from the Clustering
menu, or right-click the item and select Partitional
Clustering from the shortcut menu. The Partitional
Clustering parameters dialog is displayed.
, or select Partitional
Clustering from the Clustering
menu, or right-click the item and select Partitional
Clustering from the shortcut menu. The Partitional
Clustering parameters dialog is displayed.
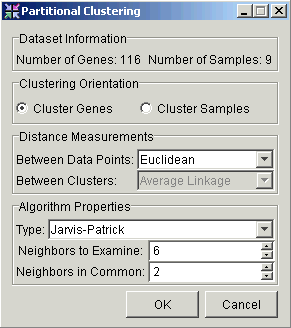
3. Set the parameters.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Clustering Orientation |
Cluster by Genes or Samples. |
|
Distance Measurements Between Data Points |
Type of distance measurement to use to determine how close two data points are to each other. |
|
Type |
Set this parameter to Jarvis-Patrick. |
|
Neighbors to Examine |
This value must be at least 2. |
|
Neighbors in Common |
This value must be at least 1, and must not exceed the value of Neighbors to Examine. |
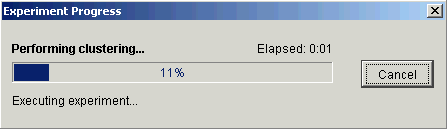
4. Click OK. The Experiment Progress dialog is displayed. It is dynamically updated as the Jarvis-Patrick Clustering operation is performed. To cancel the Jarvis-Patrick operation, click the Cancel button.
Upon successful completion, a new item is added under the original item in the Experiments navigator.
Related Topics: